Glossary: ESD
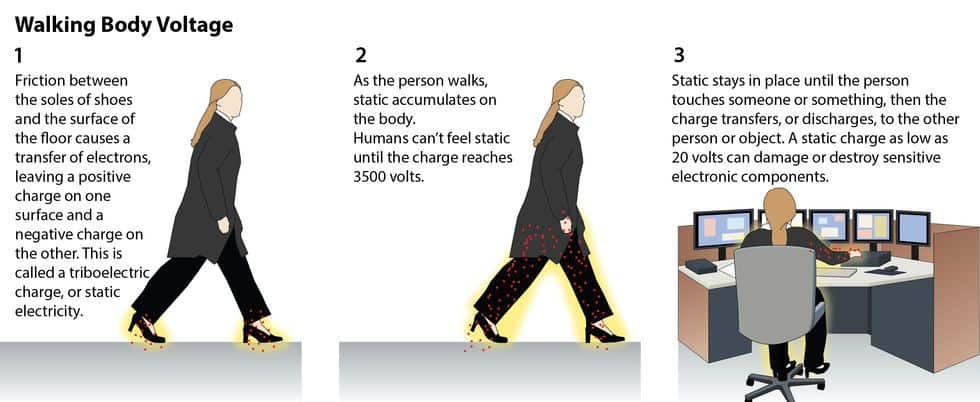
ESD is the abbreviation for electrostatic discharge.
In layman’s terms: an electrical event that takes place when two objects with different electrical potential make contact or are positioned closely enough for a spark to discharge from one surface to another. ESD events occur when people walk across various forms of flooring, then touch or approach computers and other static-sensitive electronic devices.
ESD should not be identified solely by shocks or zaps. Although shocks and zaps are ESD events, they are the result of at least thirty-five hundred (3500) volt discharges. An ESD event as low as 20 volts can disrupt electronic components. Because of this extremely low voltage, an event can go completely undetected.
ESD in the Workplace: Generating a Static Charge

Learning Center Articles
- ESD Basics
- Installation & Maintenance
- Selecting & Specifying an ESD Floor
- Technical Information
- 7 Common Mistakes Selecting an ESD floor
- A Guide to ESD Flooring Selection
- Avoid Costly Failures: What You Need to Know When Specifying ESD Flooring
- Choosing ESD Flooring for:
- ESD Footwear: What Is It and When Is It Necessary?
- ESD Footwear for Electronics Manufacturing and Handling Applications
- Facility Managers’ Guide to Selecting ESD Flooring
- The Need for Due Diligence in Specifying Static-Free Flooring
- Standard of Care for Specifying Floors in Mission-Critical Spaces
- Understanding the Hidden Costs of ESD Flooring

StaticWorx high-performance static-control floors protect electronic components, explosives, and high-speed computers from damage caused by static electricity. ESD flooring is part of a system. Choices should always be based on objective, researched evidence. When you partner with us, we look at all possible items that may need to integrate with the floor, and, focusing on your goals and objectives, help you find the right floor for your application.








