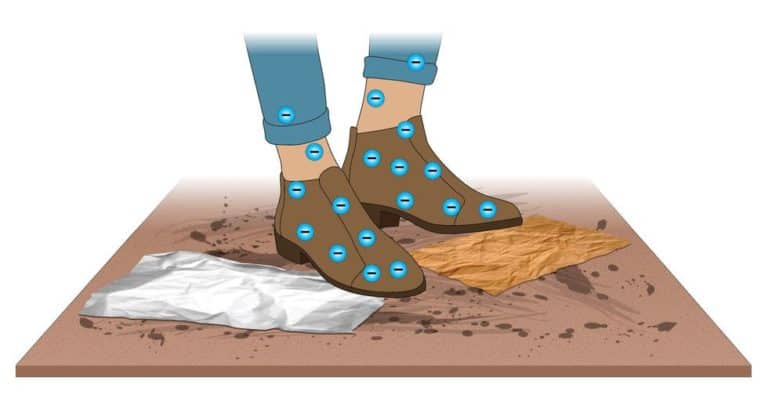
FAQ: Would I be better off with an antistatic, static-dissipative or a conductive floor?
First, let’s be clear about terms: for specificity and to help avoid confusion, the terms “static-free” or “anti-static” were recently changed to “low charge generating.” A floor described as static-free, anti-static, or low charge generation won’t contribute to triboelectrification. This means, when people walk, the floor won’t generate static on the soles of their shoes. A low-charge generating floor is not necessarily a grounded floor. Only conductive and static-dissipative materials (materials measuring < 1.0 x 10E9)—or materials that transport electrical current—can be grounded.
Grounded ESD Floor
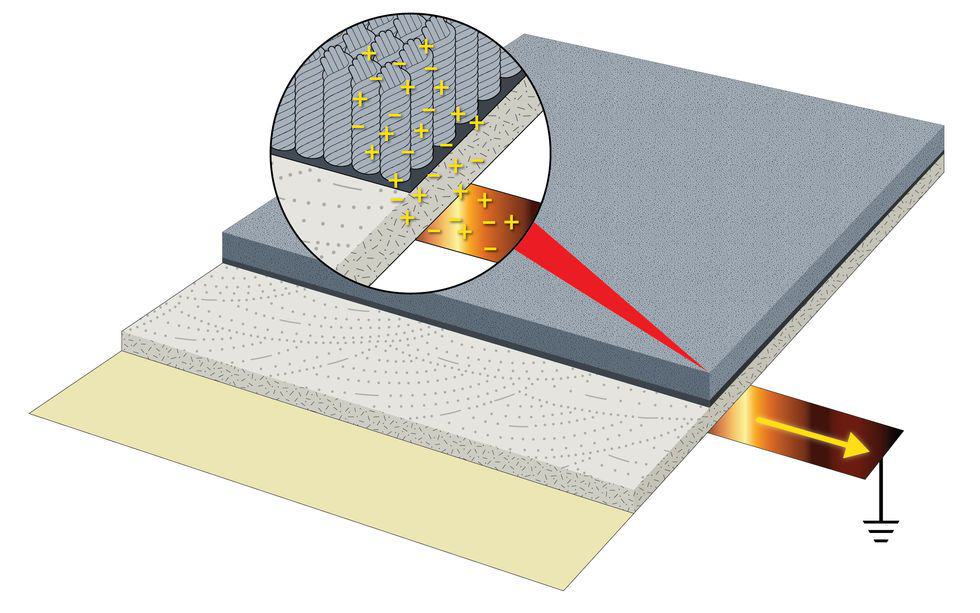

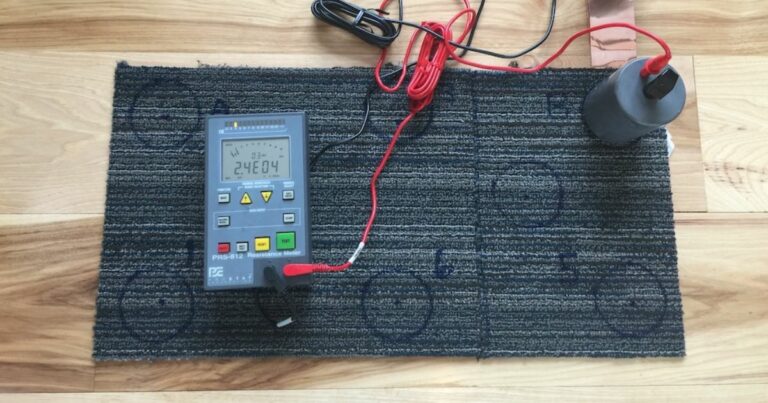
The fact that a floor exhibits low-charge-generating tendencies does not mean it will also dissipate static properly. Static dissipation, and therefore conductivity, is unrelated to charge generation; one has nothing to do with the other. The ability of a floor to discharge—or dissipate—static is related to its conductivity, which is evaluated based on electrical ohms resistance tests. Charge generation is expressed in volts.

Finding the right static-control floor means matching the floor to the specific needs of the environment. A conductive floor that performs well in an electronics facility, where people are required to wear static-protective footwear at all times, might be ineffective in a data center or 9-1-1 public safety dispatch operation where people wear regular street shoes.
These two videos should help alleviate confusion and provide a good starting point for research.


More FAQs
Learning Center Articles
- ESD Basics
- Installation & Maintenance
- Selecting & Specifying an ESD Floor
- Technical Information
- 7 Common Mistakes Selecting an ESD floor
- A Guide to ESD Flooring Selection
- Avoid Costly Failures: What You Need to Know When Specifying ESD Flooring
- Choosing ESD Flooring for:
- ESD Footwear: What Is It and When Is It Necessary?
- ESD Footwear for Electronics Manufacturing and Handling Applications
- Facility Managers’ Guide to Selecting ESD Flooring
- The Need for Due Diligence in Specifying Static-Free Flooring
- Standard of Care for Specifying Floors in Mission-Critical Spaces
- Understanding the Hidden Costs of ESD Flooring

StaticWorx high-performance static-control floors protect electronic components, explosives, and high-speed computers from damage caused by static electricity. ESD flooring is part of a system. Choices should always be based on objective, researched evidence. When you partner with us, we look at all possible items that may need to integrate with the floor, and, focusing on your goals and objectives, help you find the right floor for your application.