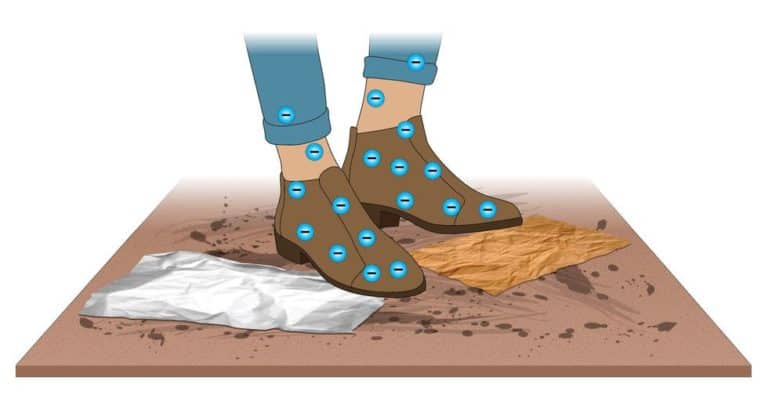
FAQ: Can you explain the differences between low static and anti-static with grounding?
Questions about the differences between “antistatic carpet” and “permanent static control” or ESD carpet are raised at some point in every project. The distinction is critical.
Flooring products are often bought with the assumption that they’re antistatic, (low charge generating), when in fact they can be, or may become, static generators. If a misapplication involves flooring for common office space or a hotel lobby, it’s no big deal. If the floor is installed in a 9-1-1 dispatch center, command center of a public utility or server room for a stock exchange, misunderstanding technical differences can have catastrophic results.
This video cartoon shows what happens when a conductive, but static-generating floor is installed in a call center or other end-user space where special ESD shoes are not mandated.


To answer this question clearly, we need to share a few pieces of information:
First, never rely on the AATCC-134 specification to judge a floors’ static-control protective properties. To protect electronic devices and equipment, static-control floors must:
- Be low charge generating – the floor must prevent the generation of static electricity
- Prove it can be grounded. A ground wire alone does NOT ground a floor. ESD flooring materials must be made with conductive elements such as carbon, carbon fibers, or other conductive materials, which provide an electrical pathway to ground.
- Must have permanent static-control properties, and its static-control properties must be independent of environmental conditions such as temperature or humidity.
- Be traffic-resistant—traffic and chair castors should not diminish the static-control performance of the floor.
- Perform without the need for special maintenance procedures such as waxing, spraying or buffing with antistatic waxes or finishes.
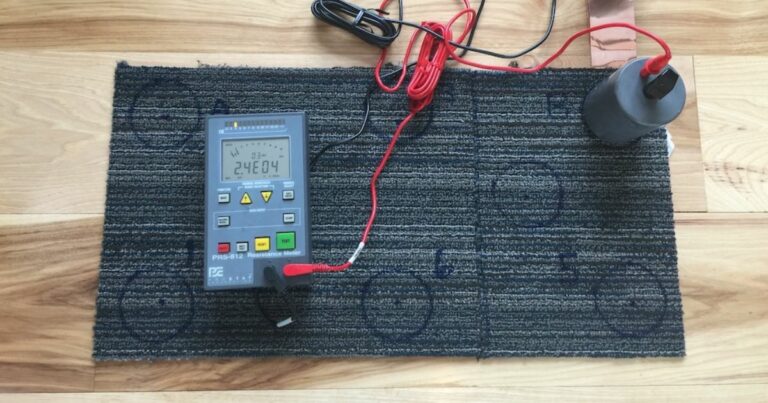
Conductive properties are easily measured with a simple, inexpensive ohm-meter.
More FAQs
Learning Center Articles
- ESD Basics
- Installation & Maintenance
- Selecting & Specifying an ESD Floor
- Technical Information
- 7 Common Mistakes Selecting an ESD floor
- A Guide to ESD Flooring Selection
- Avoid Costly Failures: What You Need to Know When Specifying ESD Flooring
- Choosing ESD Flooring for:
- ESD Footwear: What Is It and When Is It Necessary?
- ESD Footwear for Electronics Manufacturing and Handling Applications
- Facility Managers’ Guide to Selecting ESD Flooring
- The Need for Due Diligence in Specifying Static-Free Flooring
- Standard of Care for Specifying Floors in Mission-Critical Spaces
- Understanding the Hidden Costs of ESD Flooring

StaticWorx high-performance static-control floors protect electronic components, explosives, and high-speed computers from damage caused by static electricity. ESD flooring is part of a system. Choices should always be based on objective, researched evidence. When you partner with us, we look at all possible items that may need to integrate with the floor, and, focusing on your goals and objectives, help you find the right floor for your application.