Learn the differences between ESD solid vinyl tile and interlocking ESD tile. The post compares specs, installation, maintenance and intangibles.

3 Best Ways to Test an ESD Floor to Ensure Reliability
8 min read, 2 min video
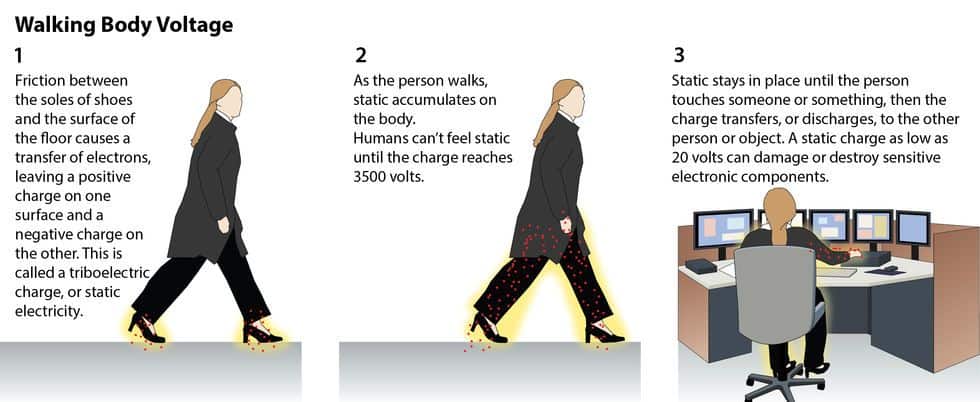
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a serious concern in many industries, particularly those that involve the manufacturing and/or handling of electronic components or sensitive equipment. ESD is typically caused by the zap that occurs when a person carrying a static charge on their body touches sensitive electronics. ESD can damage or destroy electronic components, leading to costly repairs, downtime, and lost productivity.
ESD floors are designed to prevent the buildup of static electricity and to dissipate charges from the shoes of people walking on the floor to earth ground. To ensure that an ESD floor is functioning properly, it is important to test it regularly using appropriate methods.
The following test methods ensure that your ESD floor is functioning properly and providing adequate protection against electrostatic discharge.
Electrical Resistance Test

The electrical resistance test is the most common method of testing an ESD floor. This test method, which follows procedures outlined in industry standard ANSI/ESD STM 7.1, measures the electrical resistance of the floor. Resistance in ohms should fall within a specific range based on the ESD specification appropriate to the industry.
For electronics manufacturing, the floor should measure < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
For communications facilities, PSAPs, flight towers and other end-user environments, the floor should measure > 1.0 x 10E6 and < 1.0 x 10E9.
Resistance tests are performed by placing one electrode on the floor and measuring the resistance from the probe to ground.

Resistance tests are quick and easy to perform. The key advantage of the test is that it provides a reliable indicator of the conductivity of the ESD floor and tells you whether or not the floor can transport a static charge to ground. It is important to note that the surface resistance test does not test the antistatic – or charge generation – properties of the floor. And it does not take into account the effects of environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, which can affect the conductivity of the ESD floor.
The electrical resistance test is the most common method of testing an ESD floor. This test method, which follows procedures outlined in industry standard ANSI/ESD STM 7.1, measures the electrical resistance of the floor. Resistance in ohms should fall within a specific range based on the ESD specification appropriate to the industry.
For electronics manufacturing, the floor should measure < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
For communications facilities, PSAPs, flight towers and other end-user environments, the floor should measure > 1.0 x 10E6 and < 1.0 x 10E9.
Resistance tests are performed by placing one electrode on the floor and measuring the resistance from the probe to ground.

Resistance tests are quick and easy to perform. The key advantage of the test is that it provides a reliable indicator of the conductivity of the ESD floor and tells you whether or not the floor can transport a static charge to ground. It is important to note that the surface resistance test does not test the antistatic – or charge generation – properties of the floor. And it does not take into account the effects of environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, which can affect the conductivity of the ESD floor.
Walking Body Voltage Test
The walking test is a more comprehensive way to test an ESD floor, as it simulates the movement of people on the floor. This test involves walking on the floor with special shoes with electrodes on the bottom. The shoes are connected to a charge plate meter that measures the electrical resistance, in volts, between the shoes and the floor.
For electronics manufacturing and handling facilities, the floor should generate < 100V
For end-user environments, the floor should measure < 500V.
The walking body voltage test measures the static electricity generated on shoe soles when a person walks on the floor. This test should always be performed with the test subject, in subsequent tests, wearing every type of shoes that will be allowed on the floor.
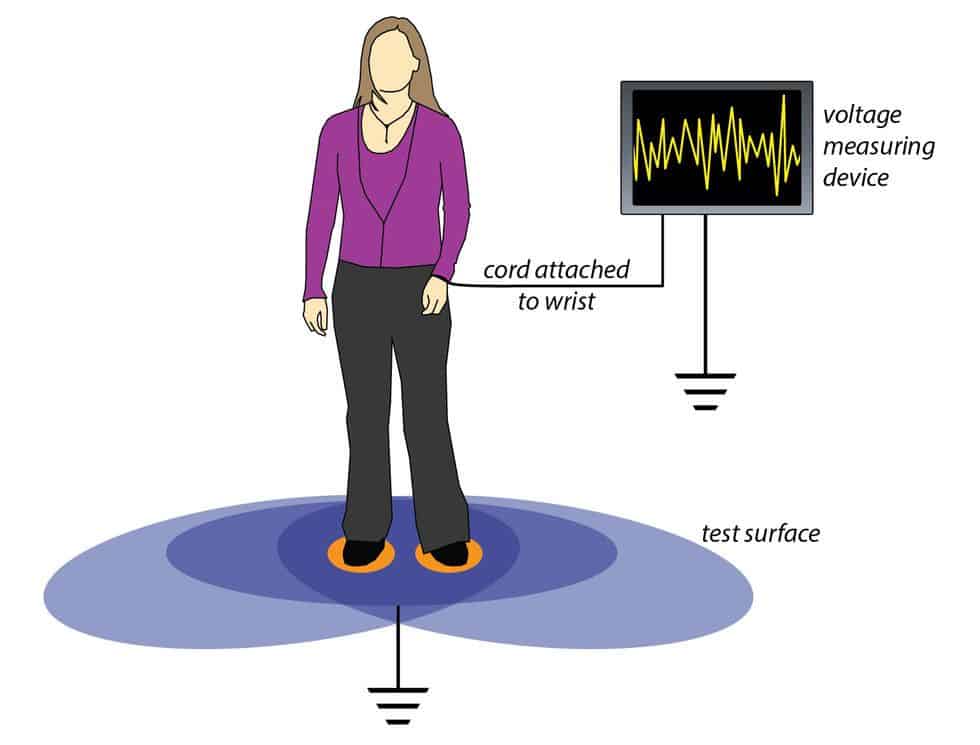
The body voltage test is a real-world test that takes into account the effects of environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, as well as the various types of (regular or ESD-preventive) shoes that will be permitted to be worn on the floor. It is more time-consuming than resistance testing and requires more expensive equipment.
One of the key advantages of the walking test is that it measures body voltage generation, a very important factor in preventing random ESD events, and provides a realistic indication of the performance of the ESD floor in real-world conditions. It can also help to identify any areas of the facility that may be more susceptible to static discharge due to environmental factors, such as low RH, or other issues.
Static Control Audit
A static-control audit looks at the floor as part of a system and is a comprehensive evaluation of the entire ESD control program. This type of extensive ESD audit is typically performed by an independent third-party consultant and provides a thorough evaluation of the ESD control program, including the effectiveness of the ESD floor.
A static control audit typically involves a detailed inspection of the ESD floor, including a review of the design, installation, and maintenance of the floor. The audit may also include resistance testing and walking body voltage tests, as well as an evaluation of the effectiveness of the overall ESD control program.
An ESD audit can help to identify any issues with the ESD system or areas of concern that may not be apparent through other testing methods. Due to the nature of the testing, it is more time-consuming and can be more expensive than other test methods.
There are several ways to test an ESD floor to ensure that it is providing adequate protection against electrostatic discharge.
- The resistance test is a simple, easy way to test an ESD floor and shows that the floor can transport a static charge to ground.
- The walking test measures static generation and provides a more realistic indication of the performance of the floor in real-world conditions.
- A static-control audit is the most comprehensive way to test an ESD floor and can help to identify any issues or areas of concern that may affect the performance of the ESD floor or compromise its integrity.
Listen
Why Resistance Tests Alone Are Not Enough to Properly Qualify an ESD Floor
Listen
Why Resistance Tests Alone Are Not Enough to Properly Qualify an ESD Floor
About StaticWorx, Inc
All StaticWorx posts are written by our technical team and based on industry standards and specifications, test data, independent lab reports and other verifiable data. We provide ESD training and offer CEU credits to architects. If you’re interested in an ESD training session or architects’ ESD workshop, give us a call: 617-923-2000.
Get in Touch
The form below will help us better understand your needs and get you as quickly as possible to the right person. We look forward to helping you solve your static problem!
You can expect a response within 24 hours. For faster service, please give us a call: 617-923-2000
"*" indicates required fields
Visit our privacy policy to find out how we process data.
More Blog Posts
To maintain performance, ESD floors require specially formulated products. We offer tips on what to consider when choosing cleaning supplies.
Static-dissipative floors transport harmful static charges to ground. Dissipative is also a term for flooring with a specific, measurable electrical resistance.
StaticWorx recognized as one of the fastest growing private companies in the U.S. 2023 marks StaticWorx fourth appearance on Inc. 5000 list.
Conductive and dissipative flooring protect electronics by transporting charges to ground, conductive at a quicker rate, dissipative slower & more controlled.
Three critical factors—application, industry standards & footwear—help you choose the best ESD floor, while ensuring the safety & efficiency of your operations.
StaticWorx Founder and President Dave Long shares three of his recommended reads: Quit, How to Change, and The Goal.
There are leadership qualities StaticWorx strives to embody every day, with every product, throughout each project.
No matter how you slice and dice a project, an ESD floor is a major investment. This blog post examines five ways to keep undue costs down.
What’s the difference between static control and static resistant? Or anti-static flooring? Find out more in our blog post.
A major part of any ESD control program is getting proper flooring in place. How can one replace a floor without generating any debris? Learn more.
A well-designed, comprehensive, fully realized program is a must for manufacturers serious about ESD control. Learn why ESD programs fail.
ESD Floors should never be specified based on the descriptive terms conductive or static dissipative. Always base ESD specs on verifiable metrics. Find out why.
To comply with relevant ESD standards, test electrical properties using methods outlined in ESD S20.20. For best results require testing by an independent lab.
If the vapor barrier fails to adhere to the subfloor, tiles will lift. Bond test and manufacturer oversight are crucial to ESD floor installation success.
Blog Post: Conductive and Static-Dissipative Flooring: What’s the Difference?
The Layperson’s Answer
What’s the difference between conductive and static-dissipative flooring? Facts, analogies and images illustrate the difference in easily understood terms.
Qualifying an ESD floor helps ensure you get the floor you paid for. Find out why you should always qualify according to ESD S20.20
Qualification is the first step in selecting an ESD floor. Learn how to perform resistance tests to be sure the floor meets electrical & safety standards.
Will bare concrete control static? Learn why concrete floors are unreliable & what precautions to take if you must work on a bare concrete floor.
A look at how the StaticWorx cartoon, 'Conductive Flooring Does Not Mean Antistatic Flooring,' was conceived and created.
Learning Center Articles
- ESD Basics
- Installation & Maintenance
- Selecting & Specifying an ESD Floor
- Technical Information
- 7 Common Mistakes Selecting an ESD floor
- A Guide to ESD Flooring Selection
- Avoid Costly Failures: What You Need to Know When Specifying ESD Flooring
- Choosing ESD Flooring for:
- ESD Footwear: What Is It and When Is It Necessary?
- ESD Footwear for Electronics Manufacturing and Handling Applications
- Facility Managers’ Guide to Selecting ESD Flooring
- The Need for Due Diligence in Specifying Static-Free Flooring
- Standard of Care for Specifying Floors in Mission-Critical Spaces
- Understanding the Hidden Costs of ESD Flooring

StaticWorx high-performance static-control floors protect electronic components, explosives, and high-speed computers from damage caused by static electricity. ESD flooring is part of a system. Choices should always be based on objective, researched evidence. When you partner with us, we look at all possible items that may need to integrate with the floor, and, focusing on your goals and objectives, help you find the right floor for your application.






























