ESD Standards and Test Methods
- Standards and Tests
- Army Corps of Engineers
- Charge Generation in Carpet
- Data Centers
- Electronics Industry
- ESDA STM
- FAA
- Health Care Industry
- Telecommunications
- U.S. Military/DoD
- ESD Footwear Requirements
- ESD Standards by Application
Introduction

Learn More About ESD Standards Here (ESDA.org)
What You’ll Find in This Section
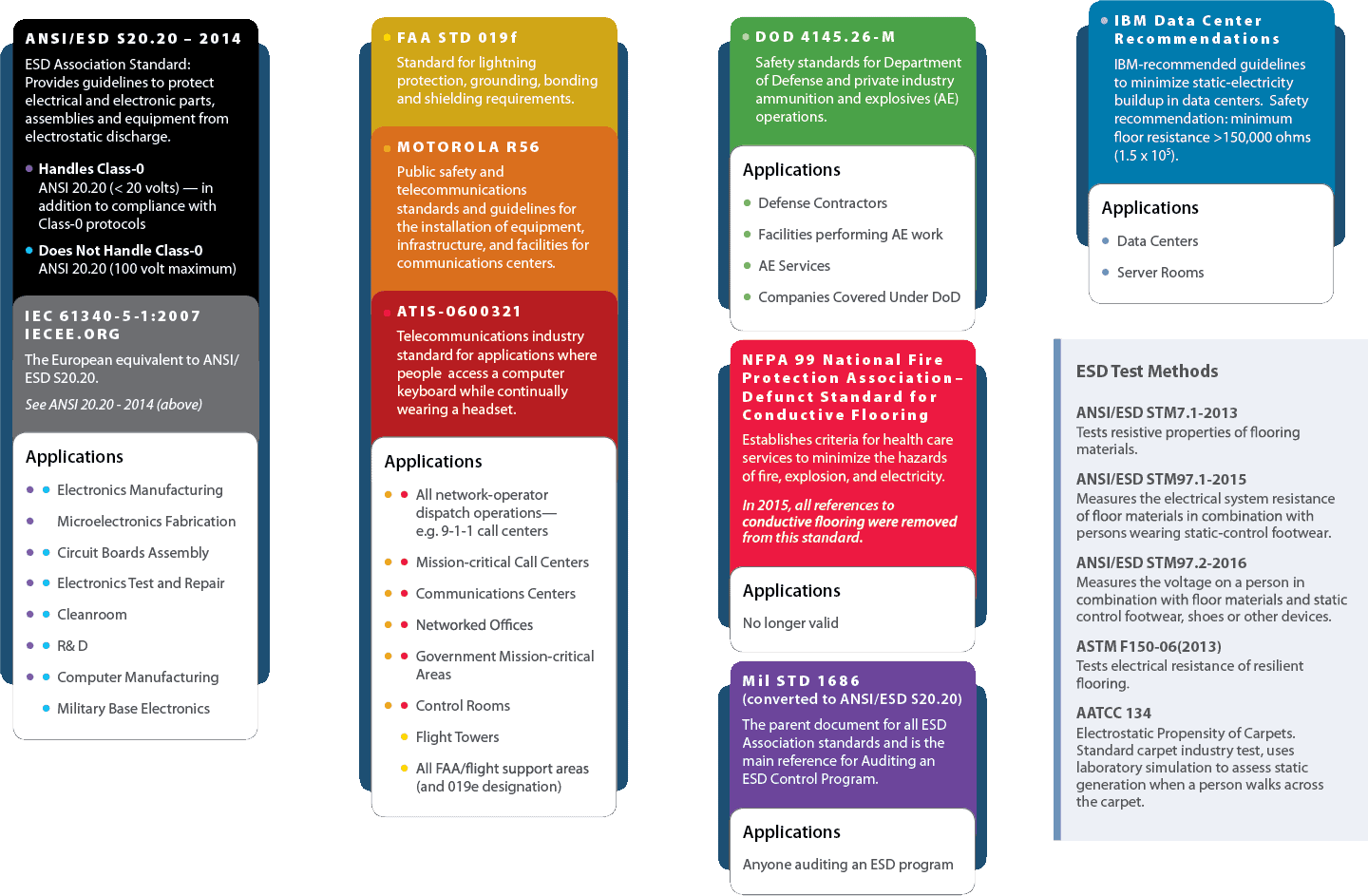
The standards and test methods included here pertain specifically to ESD floors and flooring materials. ANSI/ESD standards for wrist straps, for instance, are unrelated to ESD flooring, so we’ve left them out.
You’ll notice some variations in the standards. The telecom industry, FAA and ATIS set requirements for minimum resistance, for example, while ANSI/ESD S20.20 does not.
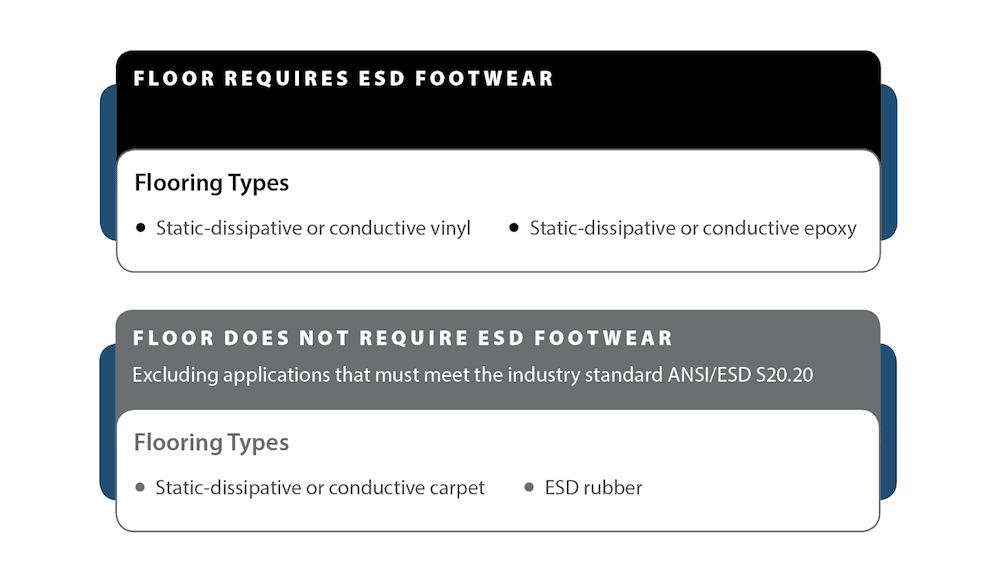
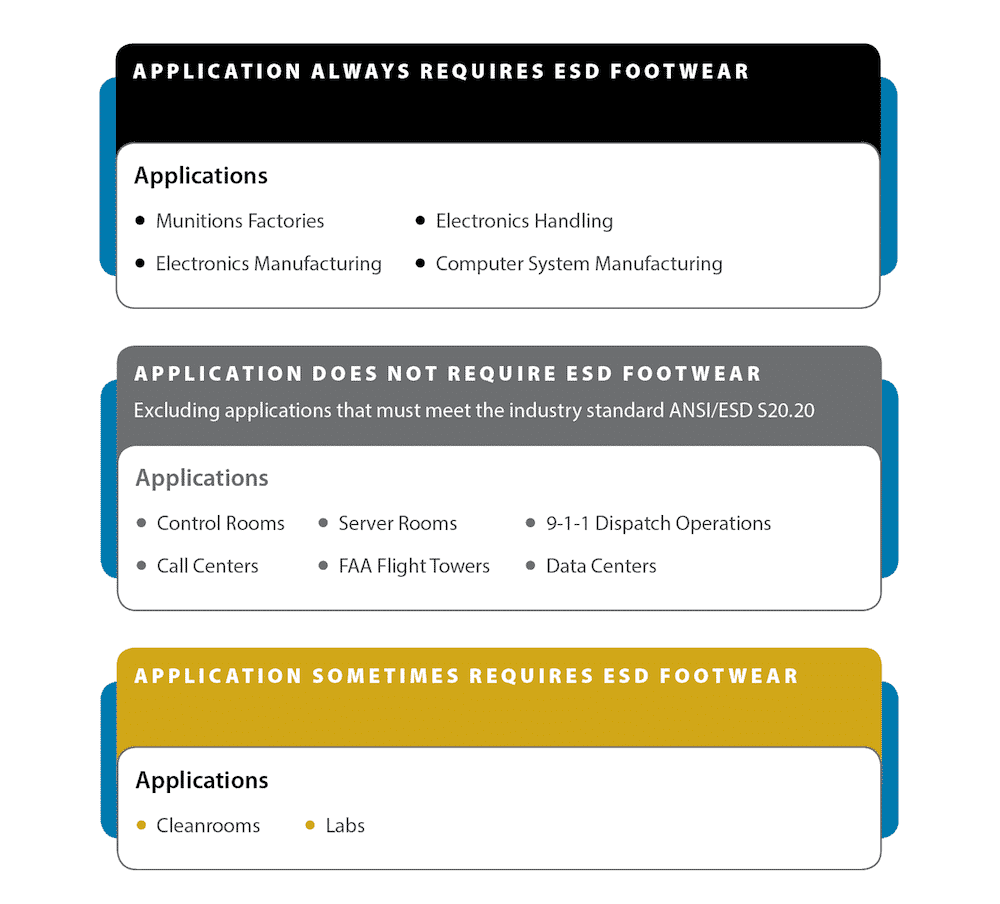
ESD-protective footwear-required in electronics manufacturing and handling environments-provide some degree of protection against electric shocks.
Under ESD Standards by Application, you’ll find a downloadable, at-a-glance chart, showing each standard with a list of applications that follow, or should follow, the parameters outlined in that standard.
- Army Corps of Engineers
- Charge Generation in Carpet
- Best Practice Recommendations for Data Centers
- Electronics Industry
- ESDA Electronics Industry Standard Test Methods (STM)
- Federal Aviation Administration
- Health Care Industry
- Telecommunications
- U.S. Military/Department of Defense
- ESD Footwear Requirements by Material and Application
- ESD Standards by Application
Army Corps of Engineers
Static-control flooring unified facilities guide specifications
Applies to: USACE / NAVFAC / AFCEC / NASA
Spec #: UFGS 09 62 38
Description: If the proper special footwear will not be worn on the static-control floor, a type of static-control flooring that provides very low static generation without special footwear should be specified. This type of flooring, such as static-control carpet, may be appropriate for mission critical areas such as 911 centers, call centers and air traffic control areas.
Specs
Conductive Vinyl Tile
Conductive vinyl tile must be a homogeneous vinyl product and conform to ASTM F1700. Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 25,000 ohms (2.5 x 10E4) and 1,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E6).
Conductive Rubber
Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 25,000 ohms (2.5 x 104) and 1,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E6).
Static-dissipative vinyl
Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 1,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E6) and 1,000,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E9).
Static-dissipative rubber
Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 1,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E6) and 1,000,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E9).
Static-control carpet
Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 25,000 ohms (2.5 x 10E4) and 100,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E8) ohms when tested in accordance with NFPA 99.
Charge Generation in Carpet
AATCC 134 Electrostatic Propensity of Carpets
This test method assesses the static-generating propensity of carpets developed when a person walks across them. This method uses controlled laboratory simulation of the conditions that may be encountered in use. The simulation is focused on the use of those conditions, which are known from experience to be strong contributors to excessive accumulation of static charges.
Best Practice Recommendations for Data Centers
IBM Data Center Recommendations: Use these guidelines to minimize static electricity buildup in your data center.
Floor covering material can contribute to buildup of high static electrical charges as a result of the motion of people, carts, and furniture in contact with the floor material. Abrupt discharge of the static charges causes discomfort to personnel and might cause malfunction of electronic equipment.
Static buildup and discharge can be minimized by:
- Maintaining the relative humidity of the room within the server operating limits. Choose a control point that normally keeps the humidity between 35 percent and 60 percent. See the Air conditioning determination for further guidance.
- Providing a conductive path to ground from a metallic raised floor structure including the metal panels.
- Grounding the raised floor metallic support structure (stringer, pedestals) to building steel at several places within the room. The number of ground points is based on the size of the room. The larger the room, the more ground points are required.
- Ensuring the maximum resistance for the flooring system is 2 x 10E10 ohms*, measured between the floor surface and the building (or an applicable ground reference). Flooring material with a lower resistance will further decrease static buildup and discharge. For safety, the floor covering and flooring system should provide a resistance of no less than 150 kilohms** when measured between any two points on the floor space 1 m (3 ft.) apart.
- Maintenance of antistatic floor coverings (carpet and tile) should be in agreement with the individual supplier’s recommendations. Carpeted floor coverings must meet electrical conductivity requirements. Use only antistatic materials with low-propensity ratings.
- Using ESD-resistant furniture with conductive casters to prevent static buildup.
* StaticWorx recommends a resistance ceiling of 1.0 x 10E9 ohms, per ANSI/ESD S20.20 (with an optimal ceiling of 1.0 x 10E8). If a floor with an electrical resistance above 10E9 were to lose conductivity–due to its makeup or environmental factors such as dry air, dirt and debris–it could become too resistant to properly discharge static to ground.
** 150 kilohms is the same as 150,000 ohms (1.5 x 10E5)
Electronics Industry
ESD Association Standard for the Development of an Electrostatic Discharge Control Program for Protection of Electrical and Electronic Parts, Assemblies and Equipment (Excluding Electrically Initiated Explosive Devices). This standard provides administrative and technical requirements for establishing, implementing and maintaining an ESD Control Program.
For ESD flooring requirements, please see the relevant Standard Test Method.
For fundamentals on electrostatic discharge and further information on ESD standards, see: Fundamentals of Electrostatic Discharge.
Revision to 2014 version change updated in 2021:
Product Qualification: Several changes were made to the requirements. Qualification for ESD control items that stay on-site can be done at the lowest RH on the site. This does not apply across multiple sites or materials that leave the site. Qualification records are now required to include supporting technical reports. Added explanation that the flooring/footwear system cannot use compliance verification data for qualification. Body voltage measurements must also be made.
Table 1: Personnel Grounding Requirement – Footwear/Flooring| Technical Requirement | Product Qualification | Compliance Verification | ||
| Test Method(s) | Required Limit(s) | Test Method(s) | Required Limit(s) | |
| Footwear/Flooring System – (Both limits shall be met)1 | ANSI/ESD STM97.1 | System Resistance < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms | ESD TR53 Footwear Section | System Resistance < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms2 |
| ANSI/ESD STM97.2 | Peak Voltage < 100 volts | ESD TR53 Flooring Section | Point to Ground Resistance < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms2 |
|
- A periodic body voltage generation test should be done to verify the voltage is less than 100 volts
- The required limit of < 1.0 x 10E9 ohm is the “maximum” allowed value. The user should document the resistance values that were measured for product qualification for the footwear and the flooring system to comply with the < 100 volts body voltage generation and use these resistances for compliance verification.
| Technical Requirement | ESD Control Item | Product Qualification | Compliance Verification | ||
| Test Method | Required Limits1 | Test Method | Required Limits | ||
| EPA | Footwear | ANSI/ESD STM9.1 | Point to Groundable Point < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms | For compliance verification of the Footwear Flooring System, see Table: Personnel Grounding Requirement | |
- For standards that have multiple resistance test methods, these limits apply to all methods.
Class-0 Electronic Devices
Class 0: Although standards organizations have not fully defined the term ESD Class 0 for manufacturing programs, the classification is widely used within the electronics industry to represent ultra-sensitive devices. While most companies are acutely aware of the hazards of ESD (electrostatic discharge), few are aware of best practices for preventing failures of today’s extremely sensitive devices often referred to as Class 0.
Floors for Class 0 applications must satisfy electrical resistance requirements in ANSI/ESD S20.20 and generate less than 20 volts of electrostatic current.
Point to Point, Point to Groundable Point, and Footwear/Flooring System: < 1.0 x 10E9
Charge Generation: < 20 volts
From IECEE.ORG: Electrostatics – Part 5-1: Protection of electronic devices from electrostatic phenomena – General requirements.
The purpose of this standard is to provide the administrative and technical requirements for establishing, implementing and maintaining an ESD control program …This [updated] version of IEC 61340-5-1 has been aligned with other major ESD control program standards used throughout the world.
Note: This is the European equivalent to ANSI/ESD S20.20
ESDA Electronics Industry Standard Test Methods (STM)
ANSI/ESD STM7.1 – 2013 ESD Association Standard Test Method for the Protection of Electrostatic Discharge Susceptible Items – Floor Materials – Resistive Characterization of Materials
This standard test method provides procedures for measuring the electrical resistance of floor materials used for the control of electrostatic charge and discharge. It also provides test methods for the qualification of floor materials prior to their installation or application, as well as test methods for acceptance and monitoring of floor materials after installation or application.
Floor Materials-Resistive Characterization of Flooring Materials in Environmentally Protected Areas (EPA).
Point to Point: < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
Point to Groundable Point: < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
ANSI/ESD STM97.1 (Resistance) ESD Association Standard Test Method for the Protection of Electrostatic Discharge Susceptible Items – Floor Materials and Footwear – Resistance Measurement in Combination with a Person.
This document provides test methods for measuring the electrical system resistance of floor materials in combination with persons wearing static control footwear.
Resistance of Footwear/Flooring System
< 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
ANSI/ESD STM97.2 (Charge Generation) ESD Association Standard Test Methods for the measurement of the voltage on a person in combination with floor materials and static control footwear, shoes or other devices.
Floor Materials and Footwear Voltage Measurement in Combination with a Person.
< 100 volts Peak
ASTM F150 – 06(2013) Standard Test Method for Electrical Resistance of Conductive and Static Dissipative Resilient Flooring
This test method covers the determination of electrical conductance or resistance of resilient flooring either in tile or sheet form, for applications such as hospitals, computer rooms, clean rooms, access flooring, munition plants, or any other environment concerning personnel-generated static electricity.
Federal Aviation Administration
FAA 019f Standard for Lightning Protection, Grounding, Bonding and Shielding Requirements for Facilities, Documents 1.4.1
Note: For use near energized equipment: 5.8.3.1 Static Conductive Materials.
Those materials with a surface resistivity less than 1.0 x 10E5 ohms per square when tested per ANSI/ESD STM11.11 shall be considered conductive. Conductive ESD control materials shall not be used for ESD control work surfaces, tabletop mats, floor mats, flooring, or carpeting where the risk of personnel contact with energized electrical or electronic equipment exists. Conductive ESD control materials shall not be used in any other application where their use could result in EMI or radio frequency interference (RFI) that would be created by rapid, high voltage ESD spark discharges.
110 ε 5.8.9 Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)Control Flooring and Floor Coverings ESD control floors and floor coverings shall have a point-to-point resistance and a surface-to-ground resistance of greater than 1.0 x 10E6 ohms and less than 1.0 x 10E9 ohms (ANSI/ESD STM7.1).
Health Care Industry
NFPA 99 establishes criteria for levels of health care services or systems based on risk to patients, staff, or visitors in health care facilities to minimize the hazards of fire, explosion, and electricity.
Requirements of NFPA 99 address installation, inspection, testing, maintenance, performance, and safe practices for facilities, material, equipment, and appliances, including medical gas and vacuum systems.
In 2015, the NFPA eliminated conductive flooring from their standard, making NFPA 99 an outdated standard for ESD flooring.
Telecommunications
Motorola R56 Public Safety and Telecommunications standards and guidelines for the installation of equipment, infrastructure, and facilities for communications sites. Appendix C: Protecting against electrostatic discharge in equipment rooms and dispatch centers.- C.3.3 FLOORING Carpeting or floor tiles within an equipment room or dispatch center, including raised flooring, should have a resistance to ground measurement of between 10E6 and 10E10 ohms when measured using the test method of ANSI/ESD STM7.1-2001 or later.
- C.3.4 CHAIRS Chairs used in dispatch centers should be ESD protective and have a resistance to ground measurement of between 105 and 109 ohms when measured using the test method of ANSI/ESD STM12.1-1997 or later. Such chairs operate in conjunction with ESD protective flooring (see previous paragraph). (ANSI T1.321-R2000, section 4.3 and ANSI/ESD STM12.1-1997).
ESD protective chairs should incorporate a continuous path between all chair elements and the ground point. The ground point of a static dissipative chair should be the static dissipative chain or the conductive casters that provide electrical continuity to the ESD flooring material. (See FAA-STD-019d2002 for additional information.)
ESDA Electronics Industry Standard Test Methods (STM)
ANSI/ESD STM7.1 – 2020 ESD Association Standard Test Method for the Protection of Electrostatic Discharge Susceptible Items – Floor Materials – Resistive Characterization of Materials
This standard test method provides procedures for measuring the electrical resistance of floor materials used for the control of electrostatic charge and discharge. It also provides test methods for the qualification of floor materials prior to their installation or application, as well as test methods for acceptance and monitoring of floor materials after installation or application.
Floor Materials-Resistive Characterization of Flooring Materials in Environmentally Protected Areas (EPA).
Point to Point: < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
Point to Groundable Point: < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
ANSI/ESD STM97.1 (Resistance) ESD Association Standard Test Method for the Protection of Electrostatic Discharge Susceptible Items – Floor Materials and Footwear – Resistance Measurement in Combination with a Person.
This document provides test methods for measuring the electrical system resistance of floor materials in combination with persons wearing static control footwear.
Resistance of Footwear/Flooring System
< 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
ANSI/ESD STM97.2 (Charge Generation) ESD Association Standard Test Methods for the measurement of the voltage on a person in combination with floor materials and static control footwear, shoes or other devices.
Floor Materials and Footwear Voltage Measurement in Combination with a Person.
< 100 volts Peak
ASTM F150 – 06(2013) Standard Test Method for Electrical Resistance of Conductive and Static Dissipative Resilient Flooring
This test method covers the determination of electrical conductance or resistance of resilient flooring either in tile or sheet form, for applications such as hospitals, computer rooms, clean rooms, access flooring, munition plants, or any other environment concerning personnel-generated static electricity.
ATIS-0600321.2020 Network Operator Dispatch Call Centers – See more at: http://standards.globalspec.com/std/9920406/atis-0600321
This telecommunications industry standard covers new installations of network operator-type equipment positions in which personnel are required to access a computer terminal keyboard while continually wearing a headset.
Measures are presented to help to control ESD in the network operator-type environment. To help minimize the effects of lightning, surges from commercial ac power lines, and power switching operations, measures are provided for equipotential bonding and grounding at the telephone Cable Entrance Facility (CEF) and the Power Entrance Facility (PEF), as well as for equipotential bonding, grounding and, where necessary, electrical protection at the network operator-type equipment position(s).
Section 4: Measures for Controlling Electrostatic Discharge 4.2 Flooring
Any carpeting or floor tiles should have a resistance to ground between 10E6 and 10E10 ohms when measured using the method of ESD-S7.1.
U.S. Military/Department of Defense
DOD 4145.26-M, March 13, 2008 “DOD CONTRACTORS’ SAFETY MANUAL FOR AMMUNITION AND EXPLOSIVES”
The Manual provides safety standards common to DoD and private industry ammunition and explosives (AE), operations, and facilities performing AE work or AE services under DoD contracts, subcontracts, purchase orders, or other procurement methods. DoD 6055.9-STD (Reference (c)) establishes these AE safety standards and serves as the primary source document for this Manual.”
C6.4. STATIC ELECTRICITY AND GROUNDING
C6.4.7.5.1. Test Criteria
The contractor can set the maximum resistance limits for the floor to the ground system and for the combined resistance of a person’s body plus the shoes, as long as the total resistance does not exceed 1,000,000 ohms [1.0 x 10E6].
C6.4.7.5.2. Minimum Resistance
To protect against electrocution, the minimum resistance of the floor to the ground system … shall exceed 40,000 ohms [4.0 x 10E4] in areas with 110 volts service and 75,000 ohms [7.5 x 10E4] in areas with 220 volts service.
Mil STD 1686 (converted to ANSI/ESD S20.20) is the parent document for all ESD Association standards and is the main reference for Auditing an ESD Control Program.
The United States Department of Defense has adopted ANSI/ESD S20.20 as a replacement for MIL-STD 1686 and ANSI/EIA-625 ESD Control Standards.
* * *
MIL-STD-1686C NOTICE 1
12 January 2021
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE STANDARD PRACTICE
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE CONTROL PROGRAM FOR PROTECTION OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PARTS, ASSEMBLIES AND EQUIPMENT (EXCLUDING ELECTRICALLY INITIATED EXPLOSIVE DEVICES)
MIL-STD-1686C, dated 25 October 1995, is hereby canceled. ANSI/ESD S20.20, “ESD Association Standard for the Development of an Electrostatic Discharge Control Program for Protection of Electrical and Electronic Parts, Assemblies and Equipment (Excluding Electrically Initiated Explosive Devices),” supersedes MIL-STD-1686C.
Link: https://www.esda.org/assets/3e74ab6e2f/MIL-STD-1686C-cancellation.pdf
Introduction

Learn More About ESD Standards Here (ESDA.org)
What You’ll Find in This Section
The standards and test methods included here pertain specifically to ESD floors and flooring materials. ANSI/ESD standards for wrist straps, for instance, are unrelated to ESD flooring, so we’ve left them out.
You’ll notice some variations in the standards. The telecom industry, FAA and ATIS set requirements for minimum resistance, for example, while ANSI/ESD S20.20 does not.
ESD-protective footwear-required in electronics manufacturing and handling environments-provide some degree of protection against electric shocks.
Under ESD Standards by Application, you’ll find a downloadable, at-a-glance chart, showing each standard with a list of applications that follow, or should follow, the parameters outlined in that standard.
Army Corps of Engineers
Static-control flooring unified facilities guide specifications
Applies to: USACE / NAVFAC / AFCEC / NASA
Spec #: UFGS 09 62 38
Description: If the proper special footwear will not be worn on the static-control floor, a type of static-control flooring that provides very low static generation without special footwear should be specified. This type of flooring, such as static-control carpet, may be appropriate for mission critical areas such as 911 centers, call centers and air traffic control areas.
Specs
Conductive Vinyl Tile
Conductive vinyl tile must be a homogeneous vinyl product and conform to ASTM F1700. Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 25,000 ohms (2.5 x 10E4) and 1,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E6).
Conductive Rubber
Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 25,000 ohms (2.5 x 104) and 1,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E6).
Static-dissipative vinyl
Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 1,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E6) and 1,000,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E9).
Static-dissipative rubber
Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 1,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E6) and 1,000,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E9).
Static-control carpet
Provide electrical resistance from surface to surface and surface to ground between 25,000 ohms (2.5 x 10E4) and 100,000,000 ohms (1.0 x 10E8) ohms when tested in accordance with NFPA 99.
Charge Generation in Carpet
AATCC 134 Electrostatic Propensity of Carpets
This test method assesses the static-generating propensity of carpets developed when a person walks across them. This method uses controlled laboratory simulation of the conditions that may be encountered in use. The simulation is focused on the use of those conditions, which are known from experience to be strong contributors to excessive accumulation of static charges.
Best Practice Recommendations for Data Centers
IBM Data Center Recommendations: Use these guidelines to minimize static electricity buildup in your data center.
Floor covering material can contribute to buildup of high static electrical charges as a result of the motion of people, carts, and furniture in contact with the floor material. Abrupt discharge of the static charges causes discomfort to personnel and might cause malfunction of electronic equipment.
Static buildup and discharge can be minimized by:
- Maintaining the relative humidity of the room within the server operating limits. Choose a control point that normally keeps the humidity between 35 percent and 60 percent. See the Air conditioning determination for further guidance.
- Providing a conductive path to ground from a metallic raised floor structure including the metal panels.
- Grounding the raised floor metallic support structure (stringer, pedestals) to building steel at several places within the room. The number of ground points is based on the size of the room. The larger the room, the more ground points are required.
- Ensuring the maximum resistance for the flooring system is 2 x 10E10 ohms*, measured between the floor surface and the building (or an applicable ground reference). Flooring material with a lower resistance will further decrease static buildup and discharge. For safety, the floor covering and flooring system should provide a resistance of no less than 150 kilohms** when measured between any two points on the floor space 1 m (3 ft.) apart.
- Maintenance of antistatic floor coverings (carpet and tile) should be in agreement with the individual supplier’s recommendations. Carpeted floor coverings must meet electrical conductivity requirements. Use only antistatic materials with low-propensity ratings.
- Using ESD-resistant furniture with conductive casters to prevent static buildup.
* StaticWorx recommends a resistance ceiling of 1.0 x 10E9 ohms, per ANSI/ESD S20.20 (with an optimal ceiling of 1.0 x 10E8). If a floor with an electrical resistance above 10E9 were to lose conductivity–due to its makeup or environmental factors such as dry air, dirt and debris–it could become too resistant to properly discharge static to ground.
** 150 kilohms is the same as 150,000 ohms (1.5 x 10E5)
Electronics Industry
ESD Association Standard for the Development of an Electrostatic Discharge Control Program for Protection of Electrical and Electronic Parts, Assemblies and Equipment (Excluding Electrically Initiated Explosive Devices). This standard provides administrative and technical requirements for establishing, implementing and maintaining an ESD Control Program.
For ESD flooring requirements, please see the relevant Standard Test Method.
For fundamentals on electrostatic discharge and further information on ESD standards, see: Fundamentals of Electrostatic Discharge.
Revision to 2014 version change updated in 2021:
Product Qualification: Several changes were made to the requirements. Qualification for ESD control items that stay on-site can be done at the lowest RH on the site. This does not apply across multiple sites or materials that leave the site. Qualification records are now required to include supporting technical reports. Added explanation that the flooring/footwear system cannot use compliance verification data for qualification. Body voltage measurements must also be made.
Table 1: Personnel Grounding Requirement – Footwear/Flooring| Technical Requirement | Product Qualification | Compliance Verification | ||
| Test Method(s) | Required Limit(s) | Test Method(s) | Required Limit(s) | |
| Footwear/Flooring System – (Both limits shall be met)1 | ANSI/ESD STM97.1 | System Resistance < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms | ESD TR53 Footwear Section | System Resistance < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms2 |
| ANSI/ESD STM97.2 | Peak Voltage < 100 volts | ESD TR53 Flooring Section | Point to Ground Resistance < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms2 |
|
- A periodic body voltage generation test should be done to verify the voltage is less than 100 volts
- The required limit of < 1.0 x 10E9 ohm is the “maximum” allowed value. The user should document the resistance values that were measured for product qualification for the footwear and the flooring system to comply with the < 100 volts body voltage generation and use these resistances for compliance verification.
| Technical Requirement | ESD Control Item | Product Qualification | Compliance Verification | ||
| Test Method | Required Limits1 | Test Method | Required Limits | ||
| EPA | Footwear | ANSI/ESD STM9.1 | Point to Groundable Point < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms | For compliance verification of the Footwear Flooring System, see Table: Personnel Grounding Requirement | |
- For standards that have multiple resistance test methods, these limits apply to all methods.
Class-0 Electronic Devices
Class 0: Although standards organizations have not fully defined the term ESD Class 0 for manufacturing programs, the classification is widely used within the electronics industry to represent ultra-sensitive devices. While most companies are acutely aware of the hazards of ESD (electrostatic discharge), few are aware of best practices for preventing failures of today’s extremely sensitive devices often referred to as Class 0.
Floors for Class 0 applications must satisfy electrical resistance requirements in ANSI/ESD S20.20 and generate less than 20 volts of electrostatic current.
Point to Point, Point to Groundable Point, and Footwear/Flooring System: < 1.0 x 10E9
Charge Generation: < 20 volts
From IECEE.ORG: Electrostatics – Part 5-1: Protection of electronic devices from electrostatic phenomena – General requirements.
The purpose of this standard is to provide the administrative and technical requirements for establishing, implementing and maintaining an ESD control program …This [updated] version of IEC 61340-5-1 has been aligned with other major ESD control program standards used throughout the world.
Note: This is the European equivalent to ANSI/ESD S20.20
ESDA Electronics Industry Standard Test Methods (STM)
ANSI/ESD STM7.1 – 2013 ESD Association Standard Test Method for the Protection of Electrostatic Discharge Susceptible Items – Floor Materials – Resistive Characterization of Materials
This standard test method provides procedures for measuring the electrical resistance of floor materials used for the control of electrostatic charge and discharge. It also provides test methods for the qualification of floor materials prior to their installation or application, as well as test methods for acceptance and monitoring of floor materials after installation or application.
Floor Materials-Resistive Characterization of Flooring Materials in Environmentally Protected Areas (EPA).
Point to Point: < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
Point to Groundable Point: < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
ANSI/ESD STM97.1 (Resistance) ESD Association Standard Test Method for the Protection of Electrostatic Discharge Susceptible Items – Floor Materials and Footwear – Resistance Measurement in Combination with a Person.
This document provides test methods for measuring the electrical system resistance of floor materials in combination with persons wearing static control footwear.
Resistance of Footwear/Flooring System
< 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
ANSI/ESD STM97.2 (Charge Generation) ESD Association Standard Test Methods for the measurement of the voltage on a person in combination with floor materials and static control footwear, shoes or other devices.
Floor Materials and Footwear Voltage Measurement in Combination with a Person.
< 100 volts Peak
ASTM F150 – 06(2013) Standard Test Method for Electrical Resistance of Conductive and Static Dissipative Resilient Flooring
This test method covers the determination of electrical conductance or resistance of resilient flooring either in tile or sheet form, for applications such as hospitals, computer rooms, clean rooms, access flooring, munition plants, or any other environment concerning personnel-generated static electricity.
Federal Aviation Administration
FAA 019f Standard for Lightning Protection, Grounding, Bonding and Shielding Requirements for Facilities, Documents 1.4.1
Note: For use near energized equipment: 5.8.3.1 Static Conductive Materials.
Those materials with a surface resistivity less than 1.0 x 10E5 ohms per square when tested per ANSI/ESD STM11.11 shall be considered conductive. Conductive ESD control materials shall not be used for ESD control work surfaces, tabletop mats, floor mats, flooring, or carpeting where the risk of personnel contact with energized electrical or electronic equipment exists. Conductive ESD control materials shall not be used in any other application where their use could result in EMI or radio frequency interference (RFI) that would be created by rapid, high voltage ESD spark discharges.
110 ε 5.8.9 Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)Control Flooring and Floor Coverings ESD control floors and floor coverings shall have a point-to-point resistance and a surface-to-ground resistance of greater than 1.0 x 10E6 ohms and less than 1.0 x 10E9 ohms (ANSI/ESD STM7.1).
Health Care Industry
NFPA 99 establishes criteria for levels of health care services or systems based on risk to patients, staff, or visitors in health care facilities to minimize the hazards of fire, explosion, and electricity.
Requirements of NFPA 99 address installation, inspection, testing, maintenance, performance, and safe practices for facilities, material, equipment, and appliances, including medical gas and vacuum systems.
In 2015, the NFPA eliminated conductive flooring from their standard, making NFPA 99 an outdated standard for ESD flooring.
Telecommunications
Motorola R56 Public Safety and Telecommunications standards and guidelines for the installation of equipment, infrastructure, and facilities for communications sites. Appendix C: Protecting against electrostatic discharge in equipment rooms and dispatch centers.- C.3.3 FLOORING Carpeting or floor tiles within an equipment room or dispatch center, including raised flooring, should have a resistance to ground measurement of between 10E6 and 10E10 ohms when measured using the test method of ANSI/ESD STM7.1-2001 or later.
- C.3.4 CHAIRS Chairs used in dispatch centers should be ESD protective and have a resistance to ground measurement of between 105 and 109 ohms when measured using the test method of ANSI/ESD STM12.1-1997 or later. Such chairs operate in conjunction with ESD protective flooring (see previous paragraph). (ANSI T1.321-R2000, section 4.3 and ANSI/ESD STM12.1-1997).
ESD protective chairs should incorporate a continuous path between all chair elements and the ground point. The ground point of a static dissipative chair should be the static dissipative chain or the conductive casters that provide electrical continuity to the ESD flooring material. (See FAA-STD-019d2002 for additional information.)
ESDA Electronics Industry Standard Test Methods (STM)
ANSI/ESD STM7.1 – 2020 ESD Association Standard Test Method for the Protection of Electrostatic Discharge Susceptible Items – Floor Materials – Resistive Characterization of Materials
This standard test method provides procedures for measuring the electrical resistance of floor materials used for the control of electrostatic charge and discharge. It also provides test methods for the qualification of floor materials prior to their installation or application, as well as test methods for acceptance and monitoring of floor materials after installation or application.
Floor Materials-Resistive Characterization of Flooring Materials in Environmentally Protected Areas (EPA).
Point to Point: < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
Point to Groundable Point: < 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
ANSI/ESD STM97.1 (Resistance) ESD Association Standard Test Method for the Protection of Electrostatic Discharge Susceptible Items – Floor Materials and Footwear – Resistance Measurement in Combination with a Person.
This document provides test methods for measuring the electrical system resistance of floor materials in combination with persons wearing static control footwear.
Resistance of Footwear/Flooring System
< 1.0 x 10E9 ohms
ANSI/ESD STM97.2 (Charge Generation) ESD Association Standard Test Methods for the measurement of the voltage on a person in combination with floor materials and static control footwear, shoes or other devices.
Floor Materials and Footwear Voltage Measurement in Combination with a Person.
< 100 volts Peak
ASTM F150 – 06(2013) Standard Test Method for Electrical Resistance of Conductive and Static Dissipative Resilient Flooring
This test method covers the determination of electrical conductance or resistance of resilient flooring either in tile or sheet form, for applications such as hospitals, computer rooms, clean rooms, access flooring, munition plants, or any other environment concerning personnel-generated static electricity.
ATIS-0600321.2020 Network Operator Dispatch Call Centers – See more at: http://standards.globalspec.com/std/9920406/atis-0600321
This telecommunications industry standard covers new installations of network operator-type equipment positions in which personnel are required to access a computer terminal keyboard while continually wearing a headset.
Measures are presented to help to control ESD in the network operator-type environment. To help minimize the effects of lightning, surges from commercial ac power lines, and power switching operations, measures are provided for equipotential bonding and grounding at the telephone Cable Entrance Facility (CEF) and the Power Entrance Facility (PEF), as well as for equipotential bonding, grounding and, where necessary, electrical protection at the network operator-type equipment position(s).
Section 4: Measures for Controlling Electrostatic Discharge 4.2 Flooring
Any carpeting or floor tiles should have a resistance to ground between 10E6 and 10E10 ohms when measured using the method of ESD-S7.1.
U.S. Military/Department of Defense
DOD 4145.26-M, March 13, 2008 “DOD CONTRACTORS’ SAFETY MANUAL FOR AMMUNITION AND EXPLOSIVES”
The Manual provides safety standards common to DoD and private industry ammunition and explosives (AE), operations, and facilities performing AE work or AE services under DoD contracts, subcontracts, purchase orders, or other procurement methods. DoD 6055.9-STD (Reference (c)) establishes these AE safety standards and serves as the primary source document for this Manual.”
C6.4. STATIC ELECTRICITY AND GROUNDING
C6.4.7.5.1. Test Criteria
The contractor can set the maximum resistance limits for the floor to the ground system and for the combined resistance of a person’s body plus the shoes, as long as the total resistance does not exceed 1,000,000 ohms [1.0 x 10E6].
C6.4.7.5.2. Minimum Resistance
To protect against electrocution, the minimum resistance of the floor to the ground system … shall exceed 40,000 ohms [4.0 x 10E4] in areas with 110 volts service and 75,000 ohms [7.5 x 10E4] in areas with 220 volts service.
Mil STD 1686 (converted to ANSI/ESD S20.20) is the parent document for all ESD Association standards and is the main reference for Auditing an ESD Control Program.
The United States Department of Defense has adopted ANSI/ESD S20.20 as a replacement for MIL-STD 1686 and ANSI/EIA-625 ESD Control Standards.
* * *
MIL-STD-1686C NOTICE 1
12 January 2021
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE STANDARD PRACTICE
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE CONTROL PROGRAM FOR PROTECTION OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PARTS, ASSEMBLIES AND EQUIPMENT (EXCLUDING ELECTRICALLY INITIATED EXPLOSIVE DEVICES)
MIL-STD-1686C, dated 25 October 1995, is hereby canceled. ANSI/ESD S20.20, “ESD Association Standard for the Development of an Electrostatic Discharge Control Program for Protection of Electrical and Electronic Parts, Assemblies and Equipment (Excluding Electrically Initiated Explosive Devices),” supersedes MIL-STD-1686C.
Link: https://www.esda.org/assets/3e74ab6e2f/MIL-STD-1686C-cancellation.pdf
Get in Touch
The form below will help us better understand your needs and get you as quickly as possible to the right person. We look forward to helping you solve your static problem!
You can expect a response within 24 hours. For faster service, please give us a call: 617-923-2000
"*" indicates required fields
Visit our privacy policy to find out how we process data.
Learning Center Articles
- ESD Basics
- Installation & Maintenance
- Selecting & Specifying an ESD Floor
- Technical Information
- 7 Common Mistakes Selecting an ESD floor
- A Guide to ESD Flooring Selection
- Avoid Costly Failures: What You Need to Know When Specifying ESD Flooring
- Choosing ESD Flooring for:
- ESD Footwear: What Is It and When Is It Necessary?
- ESD Footwear for Electronics Manufacturing and Handling Applications
- Facility Managers’ Guide to Selecting ESD Flooring
- The Need for Due Diligence in Specifying Static-Free Flooring
- Standard of Care for Specifying Floors in Mission-Critical Spaces
- Understanding the Hidden Costs of ESD Flooring

StaticWorx high-performance static-control floors protect electronic components, explosives, and high-speed computers from damage caused by static electricity. ESD flooring is part of a system. Choices should always be based on objective, researched evidence. When you partner with us, we look at all possible items that may need to integrate with the floor, and, focusing on your goals and objectives, help you find the right floor for your application.